In a world driven by data, anomalies are like sudden spikes in a heart monitor—they may signal something critical or simply an out-of-place blip. The challenge for data scientists is distinguishing between harmless noise and patterns that demand attention. Traditional statistical methods often stumble when datasets grow in size and complexity. This is where the Isolation Forest algorithm enters the stage—a method that doesn’t just look for outliers but actively isolates them with the precision of a detective separating suspects from the crowd.
The Forest That Sees What Others Miss
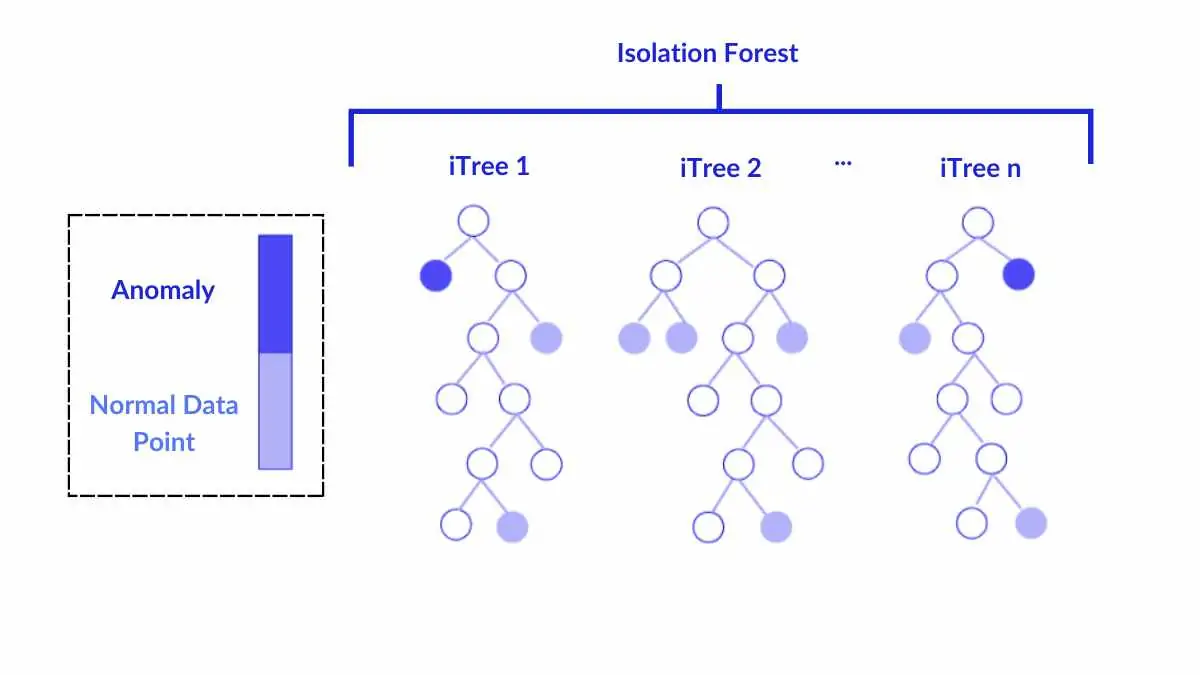
Imagine walking through a dense forest, where each tree represents a decision path. As you move deeper, every fork in the path separates one data point from another—like peeling away layers until only the most unique ones remain. This is how the Isolation Forest works.
Instead of profiling what’s “normal,” it isolates the rare or unusual. Each tree in the ensemble makes random cuts in the data space. Outliers, being distinct, are easier to separate—they get isolated in fewer splits. In contrast, normal points take longer to isolate because they blend with the crowd.
This tree-based efficiency makes the Isolation Forest ideal for handling high-dimensional data, where traditional distance-based methods like k-means or DBSCAN struggle to define “closeness.”
Students learning through a data science course in Mumbai often find this algorithm a breakthrough—because it reframes anomaly detection not as measuring deviation, but as finding isolation paths.
How Isolation Forest Differs from Traditional Models
Most anomaly detection algorithms rely on calculating distances or densities to identify unusual data points. The Isolation Forest takes a radically different path. Rather than analysing similarity, it focuses on separation.
- Random Partitioning: It randomly selects a feature and a split value between the feature’s minimum and maximum.
- Isolation Depth: The fewer splits required to isolate a data point, the more anomalous it is considered.
- Scalability: Unlike computationally heavy algorithms, Isolation Forest handles large datasets efficiently with linear time complexity.
This elegant simplicity has made it a staple in fraud detection, network security, and manufacturing quality checks—domains where detecting the rare early can prevent massive losses later.
Visualising Isolation: When Intuition Meets Mathematics
Think of an airport security system that screens passengers. Regular travellers pass through smoothly—they fit expected patterns. But a traveller carrying something unusual is pulled aside quickly for inspection. Similarly, the Isolation Forest algorithm flags outliers early because they don’t conform to the majority’s flow.
Each decision tree acts like a checkpoint. By averaging results from all trees, the algorithm produces an anomaly score. Points with scores close to 1 are potential outliers, while those near 0 are typical observations.
The technique aligns beautifully with the human approach to anomaly detection—observe, separate, and investigate.
Practical Applications Across Industries
The beauty of the Isolation Forest lies in its versatility. In finance, it detects credit card fraud by spotting transactions that differ subtly from usual spending behaviour. In healthcare, it helps identify abnormal patient readings that may indicate early symptoms of disease. In cybersecurity, it recognises unusual login patterns that could signal intrusions.
Professionals trained through a data science course in Mumbai often apply this method to real-world datasets—from detecting machine faults in IoT systems to analysing consumer behaviour anomalies in e-commerce platforms. Its interpretability and computational efficiency make it indispensable for both academic research and business intelligence.
Challenges and Considerations
No algorithm is flawless, and Isolation Forest is no exception. Its performance depends heavily on parameter tuning—such as the number of trees and sample size. A poorly configured model might overfit, labelling too many normal points as anomalies.
Moreover, in datasets with overlapping clusters or evolving data patterns, isolation may not always reflect true abnormality. Therefore, combining Isolation Forest with domain knowledge or hybrid approaches (like autoencoders or clustering) often yields the best outcomes.
Conclusion
Anomalies are the stories that data whispers, and the Isolation Forest listens carefully. It doesn’t rely on predefined norms—it lets patterns emerge organically, separating the outliers with quiet precision.
As data grows in complexity, mastering such algorithms will be essential for professionals who want to stand out in the analytics world. Understanding how isolation reveals insight is not just a technical skill—it’s an art of interpretation.
Individuals who engage in structured learning acquire not only theoretical knowledge but also practical skills, enabling them to apply this approach across various industries. Ultimately, in the vast landscape of data, those who can identify the rare insights are the ones who uncover the most valuable truths.